What is GMP?
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) is the part of quality assurance that ensures consistent quality standards in the production and testing of medicinal products or active ingredients (APIs).
This is a short excerpt from the eLearning course on GMP basics. You will find more information about this GMP E-Learning Course here.

Human health is the primary concern. In everyday life, patients must feel they can rely on the high quality of a medicinal product, as they cannot check this themselves. The quality of a medicinal product is determined above all by the following factors:
- Identity (are the specified ingredients contained?)
- Content (are the ingredients present in the specified quantity?)
- Purity (is the product free of ingredients that do not belong in it?)
The EU Guidelines to Good Manufacturing Practice require that “The holder of a Marketing Authorisation must manufacture medicinal products so as to ensure that they are fit for their intended use, comply with the requirements of the Marketing Authorisation or Clinical Trial Authorisation, as appropriate and do not place patients at risk due to inadequate safety, quality of efficacy.”
This must be proven to the competent authority, which grants approval for the medicinal product, because: without marketing authorisation, a medicinal product may not be marketed to patients. How can these requirements therefore be met? And: how can consistent quality be ensured if it is not possible to individually test each tablet that is pressed? This is the purpose of good manufacturing practice.
The principles of good manufacturing practice apply to almost all areas of a company, from research and development to production, quality control, storage and distribution. Anyone who manufactures, tests, stores or markets medicinal products or APIs on a commercial basis must therefore implement a series of defined requirements. The basic principle is that companies must manufacture medicines in such a way that they are suitable for their intended use.
Where does GMP come from?
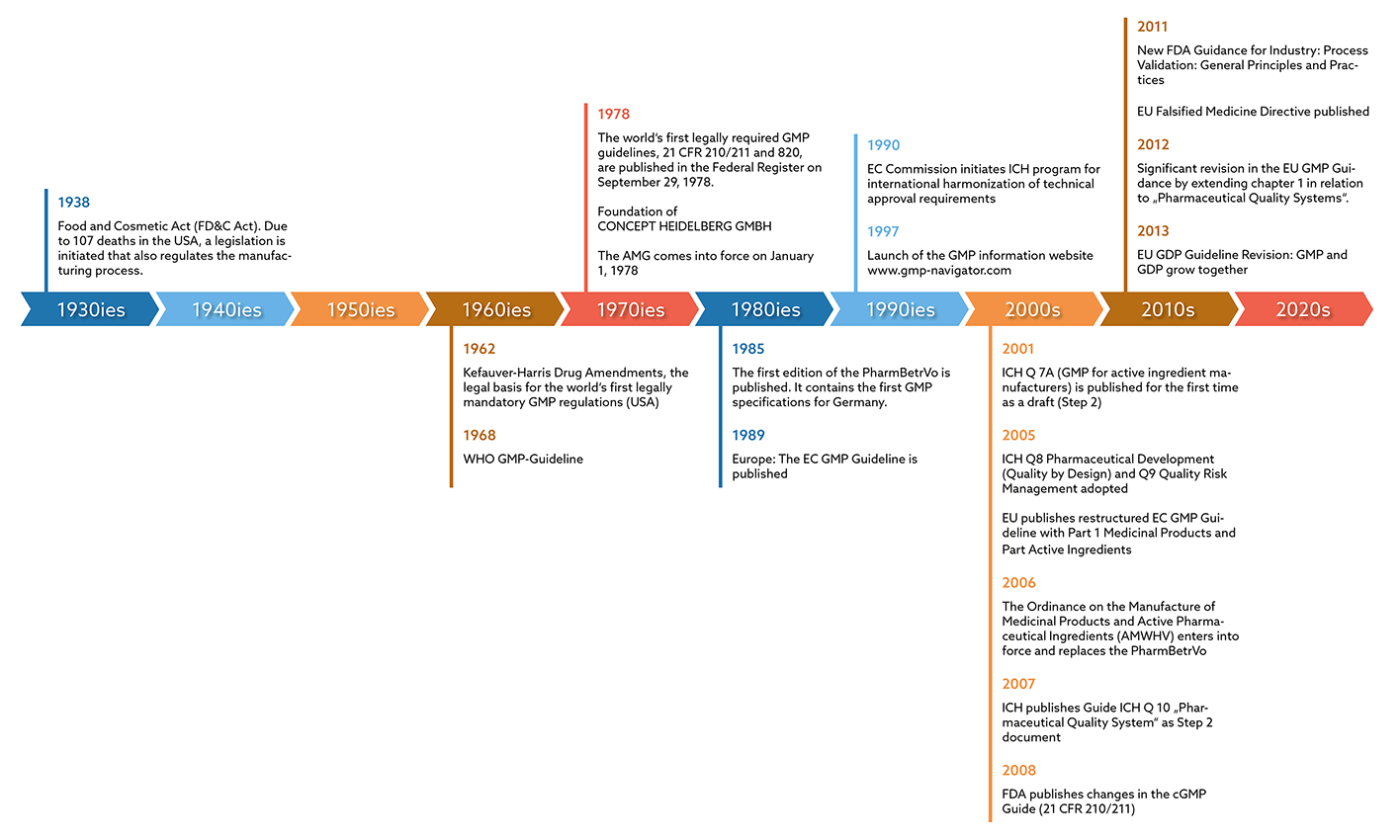
The basis for GMP requirements is the CGMP (Current Good Manufacturing Practice) Guide, which the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) published in the Federal Register in 1978. With this, the authority had created the world's first legally anchored GMP regulations. These made it possible for the manufacturing processes of pharmaceutical companies to be monitored by a regulatory authority.
However, the topic also gained importance internationally: In Germany, for example, the German Medicines Act (AMG) was published in 1978 as a direct result of the thalidomide scandal. However, it did not yet contain any specific GMP requirements. It was not until 1985 that the “Pharma-Betriebsverordnung” was published. For the first time, this contained concrete GMP specifications for Germany, which formed the basis for GMP monitoring through inspections by the responsible authorities. It took another four years before the EC GMP Guidelines, which are binding for Europe, finally appeared in 1989. According to the German AMWHV §2, the guideline is now called the EU GMP Guideline and has been legally valid in Germany since 2005, which means that compliance with its specifications must be documented.
Frequently asked questions - Table of contents
What does GMP stand for?
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practice. Manufacturers of medicinal products and active substances must comply with GMP guidelines during production, processing, testing, packaging and storage. The aim is to ensure that patients can rely on medicines always meeting the same, highest quality standards.
What are GMP rules?
GMP rules are the requirements for quality assurance of the manufacturing processes and environment formulated by the European Commission in the principles and guidelines of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) for medicinal products for human use and active pharmaceutical ingredients. The EU GMP Guide describes how these rules are to be interpreted in Part I for medicinal products and in Part II for active substances, as well as in various annexes for specific product groups.
Where is GMP applied?
GMP applies in the pharmaceutical industry as well as in the cosmetics and food industries. So, in addition to pharmaceutical manufacturers, cosmetics and food manufacturers must also apply the principles of Good Manufacturing Practice in production, quality assurance and control, ensuring that their materials and products are safe for the consumers. However, it is important to emphasize that the requirements are different for the above industries. Medicines are subject to particularly strict rules to ensure patient safety.

Where are the GMP requirements defined?
The European Commission has summarized the GMP requirements in the EU GMP Guide, which was published in Europe in 1989. Part 1 of the guide covers the manufacture of medicinal products, Part 2 the manufacture of Active Substances used as Starting Materials. Further 19 annexes address specific product groups (e.g. sterile medicinal products, biological medicinal products) or contain further specifications, e.g. for computerised systems). Part 3 contains GMP related documents, which clarify regulatory expectations. It is intended to host a collection of GMP related documents, which are not detailed guidelines on the principles of GMP.
Does GMP also apply to manufacturers of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)?
Yes, GMP also applies to companies that manufacture active pharmaceutical ingredients that are processed in medicinal products. For this purpose, the EU GMP Guideline has Part II - Basic Requirements for Active Substances used as Starting Materials. This is based on Article 46(f) of Directive 2001/83/EC and Article 50 (f) 2001/82/EC as amended by Directive 2004/27/EC and 2004/28/EC respectively. They are also subject to GMP monitoring. However, the performance of a GMP inspection is not a prerequisite for the issuance of a manufacturing license, as is the case for medicines. In the case of APIs, the authority itself decides when an inspection is to be carried out. For some APIs, though, an exception applies in some EU member States, e.g. for APIs that are of animal, human or microbial origin or that are produced by genetic engineering. In this case, a manufacturing authorisation is required under national medicinal product laws or, in the case of imports, a certificate under these laws, but monitoring is carried out in the same way.
Where are the GMP requirements for active pharmaceutical ingredient manufacturers defined?
The GMP requirements for manufacturers of active pharmaceutical ingredients are also defined in the EU GMP Guideline. The guide is divided into two parts. Part I regulates the manufacture of medicinal products, and Part II regulates the manufacture of Active Substances used as Starting Materials.
What is a GMP guideline?
Guidelines provide guidance on the scientific or regulatory aspects of the development of medicines and applications for marketing authorisation. Although guidelines are not legally binding, applicants need to provide justification for any deviations.
Detailed guidelines in accordance with principles laid down in the respective Directives are published in the EU Guidelines for Good Manufacturing Practice which will be used in assessing applications for manufacturing authorisations and as a basis for inspection of manufacturers of medicinal products.
What is the difference between GMP and CGMP?
In the USA, people often refer to cGMP (or CGMP) instead of GMP. The "C" stands for "current". According to the FDA, the CGMP requirements have been designed to be flexible enough to allow each manufacturer to decide how best to implement them. Accordingly, the "C" in CGMP stands for "current", which means that it is up to the manufacturer to keep up to date ("current") with the help of Guides and Guidances, Inspectional Guidelines, Warning Letters, FDA presentations and workshops, etc. and that they must use technologies and systems that are up-to-date to comply with the regulations. Systems and equipment that were "top-of-the-line" 10 or 20 years ago to avoid contamination, mix-ups and errors may be inadequate by today's standards. The expectations of the EU are to be understood more clearly.

Who developed GMP?
In 1962, the Kefauver-Harris Drug Amendments formed the legal basis for the world's first legally required GMP rules in the USA. However, there were still no concrete guidelines with recommendations for implementation. The WHO published the first GMP guidelines in the same year, though. These were of no legal significance, since there was no legal obligation to implement the GMP requirements in the manufacture of medicines. Finally, in 1978, the cGMP Guide of the American Food & Drug Administration (FDA) was published in the Federal Register. With this, the authority had created the world's first legally anchored GMP regulations. These made it possible for the manufacturing processes of pharmaceutical companies to be monitored by a regulatory authority.
In Europe, the EC GMP Guidelines, which were binding, were finally published in 1989.
Is GMP a law?
Yes, Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) is a requirement in the European Union (EU). However, it is not a single law but a set of regulations, directives and guidelines that ensure the quality and safety of medicinal products and active substances. A "regulation" is a binding legislative act. It must be applied in its entirety across the EU. A "directive" is a legislative act that sets out a goal that all EU countries must achieve. However, it is up to the individual countries to devise their own laws on how to reach these goals.
Other than in the EU, in the USA the GMP Guidelines are reviewed every year to ensure that they are up to date and modified if necessary – therefore the “CGMP” for “current GMP”. The CGMP is laid down in the form of a law in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), the collection of US legal texts, under 21 CFR 210 and 21 CFR 211. In addition, there are other chapters of the CFR that are relevant in the context of GMP (e.g. 21 CFR 11, or 21 CFR 820).
Is GMP mandatory?
In the EU, compliance with GMP is mandatory for pharmaceutical manufacturers and is a prerequisite for obtaining and maintaining marketing authorization for their products.
Non-compliance with GMP can lead to regulatory actions, including warnings, fines, suspension or revocation of manufacturing licenses, and product recalls. GMP ensures that manufacturers maintain high standards of quality throughout the production process, from sourcing raw materials to the final product's distribution, thereby safeguarding public health and ensuring the reliability of the products in the market.
If the company also exports its products to the USA, the US FDA GMP Guide must also be applied. Otherwise there could be problems with approvals or importing the products into the USA.
Who monitors GMP compliance?
Regulatory authorities, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and national competent authorities, enforce GMP regulations through inspections of manufacturing facilities.
In France, for example, this is the Agence nationale de sécurité du medicament et des produits de santé (ANSM). The authority regulates the monitoring of all aspects of public health. As part of this task, the agency also ensures the safety, efficacy, quality and proper use of public health products.
In Germany, the monitoring is the responsibility of the federal states. As a rule, the local authority (Regierungspräsidium or Bezirksregierung) is responsible for this – based on the production site for the specific medicinal product. A production site in Frankfurt, for example, is monitored by the Darmstadt local authority. A list of the competent federal state authorities can be found on the website of the "Zentralstelle der Länder für Gesundheitsschutz bei Arzneimitteln und Medizinprodukten" (ZLG).
Who carries out GMP Inspections?
A GMP inspection in the pharmaceutical environment can only be carried out by a state authority (competent authority). Accredited bodies that carry out ISO audits, for example, are not allowed to initiate official GMP inspections or certify GMP conformity. There is also no GMP certification / no GMP certificate from the authority, but there is a confirmation. The official name is: "Confirmation of a manufacturer's compliance with GMP". Colloquially, this is often referred to as "GMP certificate". The basis for the implementation is the EU GMP Directive 2001/83/EC.
In Germany this directive has been transposed into national law. The authorities inspect on the basis of the requirements in EU Directive 2003/94 EC. The concrete interpretation for Germany can be found in the EU GMP Guideline including the annexes. In Germany, the Ordinance on the Manufacture of Medicinal Products and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (Arzneimittel- und Wirkstoffherstellungsverordnung) is also used for implementation. This was enacted in order to have a concrete implementation regulation. This implementing regulation also contains, e.g. in § 42, the catalogue of administrative offences in the event that companies violate the GMP requirements.
What is a GMP Certificate?
Unlike the ISO standard, manufacturers of medicinal products are not "GMP certified". However, the competent authority can issue a WHO GMP certificate to a company that has a manufacturing licence - i.e. operates and is supervised according to GMP - at the manufacturer's request. Pharmaceutical manufacturers often need these certificates for export, as customs of non-EU countries usually request these certificates. Therefore, WHO certificates are often also called export certificates.
Further, also companies that develop equipment for pharmaceutical production or carry out other manufacturing-related activities also do not receive a GMP certificate. The pharmaceutical entrepreneur is responsible for selecting service providers and suppliers who offer GMP-compliant services. As part of a supplier qualification, the entrepreneur must prove that he initially and, following, also regularly monitors the selected suppliers. For this purpose, the pharmaceutical entrepreneur must choose a risk-based approach. In the case of suppliers whose products have a low potential risk for patient safety, the review can be carried out e.g. via self-assessment questionnaires. For services that potentially pose a high risk to patient safety, a GMP review of the supplier through a GMP audit may be required.
What is GMP certified?
The term "GMP-certified" does not exist per se. Nevertheless, "GMP certificate" is often used for the "confirmation of a manufacturer's compliance with GMP" issued by the official authority.
What is a GMP Qualification?
Both the EU GMP Guide and the CGMP Guide of the US FDA require that manufacturers have sufficient personnel with the necessary qualifications and practical experience. Employees who work in the production, testing and storage of medicinal products or active pharmaceutical ingredients must therefore be qualified for their respective tasks and receive ongoing training. For this reason, every pharmaceutical company must establish a comprehensive training system that plans and documents GMP training.
With respect to equipment, qualification is an action of proving that any equipment works correctly and actually leads to the expected results. The word validation is sometimes widened to incorporate the concept of qualification.
What is a GMP Audit?
GMP audits are a central element in the pharmaceutical industry for implementing quality assurance measures. An audit can identify and eliminate weak points and thus ensure that the company in question is working to guarantee the quality and safety of its products. According to the EU GMP Guide, Part I, Chapter 9, “Self inspections should be conducted in order to monitor the implementation and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice principles and to propose necessary corrective measures.”
What is GMP-compliant Documentation?
Good documentation constitutes an essential part of the quality assurance system and is key to operating in compliance with GMP requirements. The various types of documents and media used should be fully defined in the manufacturer's Quality Management System.
Documentation may exist in a variety of forms, including paper-based, electronic or photographic media. The main objective of the system of documentation utilized must be to establish, control, monitor and record all activities which directly or indirectly impact all aspects of the quality of medicinal products (see EU GMP Guidelines Chapter 4: Documentation). What is a Manufacturing and/or Import Licence?
Companies that manufacture medicinal products in compliance with GMP requirements receive a manufacturing authorisation. If the production site is outside the EU but manufactures medicinal products in compliance with EU GMP, the company is granted an import permit. Compliance with GMP requirements is checked before a medicine is imported for the first time. In addition, GMP inspections are carried out regularly (every two years according to EU regulations) to check compliance with the GMP guidelines.
What is GDP?
Good Distribution Practice (GDP) is the sum of measures that ensure that the quality and integrity of medicinal products is maintained by controlling the distribution chain. Although the EU GDP guideline is primarily aimed at the wholesale trade of medicinal products, the implementation of the requirements must be ensured equally by all participants in the distribution chain. Therefore, pharmaceutical manufacturers and any parties involved in logistics (transport companies, warehouses, etc.) must also comply with the GDP requirements if they are involved in the distribution of medicinal products. The EU Commission has also formulated a guideline for active pharmaceutical ingredients. This is entitled "Principles of Good Distribution Practice for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients for Human Use".
The GDP requirements are monitored by the GMP/GDP inspectorates of the individual countries. Within the framework of GDP inspections, it is checked whether they have been implemented in operational practice according to the requirements of the Guideline. For this purpose, the premises, processes and, above all, the specification and verification documentation are checked on a regular basis.
What is the GMP Directive?
With the European Union (EU) GMP Directive 2017/1572, the EU aims to standardise GMP requirements for manufacturers of medicinal products in all EU member states. However, EU directives must be transposed into national law in the individual member states. This was done, for example, in Germany via the AMWHV and in Austria via the AMBO. The EU GMP Directive is relatively "slim" with seven pages, but with its structure in
- Pharmaceutical Quality System
- personnel
- Premises and Equipment
- Documentation
- Production
- Quality Control
- Outsourced Activities
- Complaints and Product Recall
- Self Inspection
already provide the framework for pharmaceutical manufacturers. In addition to the implementation in the AMWHV, for example, the EU GMP Guideline with its annexes also provides interpretation assistance for these nine paragraphs mentioned above.
Training
For manufacturers of medicinal products or active pharmaceutical ingredients, this means that they have to train their employees appropriately for the GMP-compliant performance of their tasks. This training is intended to ensure that production employees learn the GMP specifications that are important for their area of operation and know how to implement them after successfully completing the course. Proof must also be provided for this training. The ECA Academy supports companies worldwide in this and offers a wide range of GMP training courses, advanced training and conferences. Starting with the GMP basics and going down to the details, the courses impart GMP knowledge with regard to production, documentation, quality management, microbiology, aseptics, storage, etc. For some time now, we have also been offering our seminars as online training courses, conferences and webinars. Find out more about our courses and conferences, which you can also find under the menu item Seminars.
